Applications of “SANGEOTEX” Geotextiles
“SANGEOTEX” geotextile is produced from staple polyester or polypropylene fibers which are bonded by either needle-punching or thermally. Special production technology of “SANGEOTEX” geotextile allows achieving optimal distribution of the fibers with further formation of the canvas. Unlike many other producers, our company takes advantage of modern production technology, which guarantees high quality and durability of the material.
Main Functions of “SANGEOTEX” geotextiles
Reinforcement. The geotextiles enhance the bearing capacity of the subgrade road constructions, slopes, reducing the strain of coatings and rutting. Since “SANGEOTEX” geotextile provides uniform load distribution of vehicles and the self-weight of the roadway, a significant reinforcement of the road constructions takes place. A particularly relevant field of application with regard to this property is road construction on weak grounds.
Separation. The use of “SANGEOTEX” geotextiles leads to separation of soil layers, preventing them from mixing with each other and slowing the process of soil erosion. Possible interpenetration of particles from adjacent pavement layers to each other is excluded; for example, a sand layer is not mixed with a layer of gravel. As a result, the geotextile actually reduces the amount of bulk material, by reducing its “sinking” in the ground.
Drainage.
The application of “SANGEOTEX” geotextiles enables a change of the hydrothermal regime of the canvas, preventing siltation of drainage layer of pavement as well as drainage acceleration.
Filtration.
SANGEOTEX geotextile prevents the penetration of soil in filtration and drainage structures. Hence, soil particles are unlikely to penetrate into existing structures in the road system of perforated drains. In addition, so-called “reverse filtering” (i.e. penetration of particles from the drainage system into the roadbed) emerges.
Main application areas of „SANGEOTEX“ geotextiles
|
Road Construction
|
|
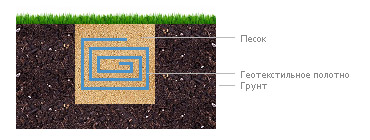
Forms a separating layer between the lower ground
and bulk materials
|
prevents flooding of bulk material by soil particles, permitting the
bulk material to retain its function of load balancing and stability;
prevent uneven penetration of bulk material into the soil which aids
to reduce material consumption;
optimizes the sealing so that the bulk material does not penetrate
into the ground;
used as a filter between the ground and the drain filler;
prevent flooding of drainage aggregate or drainage
pipes by soil particles;
forms a reinforcing layer on a soft, non-cohesive
soils;
prevent the collapse of slopes;
allows the construction of roads, even on soft soil;
reduces the deformation of roadway.
|
|
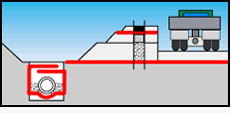
Tunnel Construction
|
|

Forms a protective drainage layer between the rock
and the protective coatingм
|
protects the insulating coating from damage caused
by rough concrete surface;
protects the insulating coating from damage caused
by sharp filler;
reduces stress between the concrete lining and
rocks;
diverts dirt and storm water to drain.
|
|
Hydraulic Construction
|
|
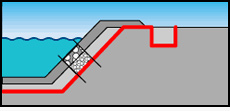
Performs the function of an inverse filter under
embankments
|
prevents water erosion of soil;
prevents erosion in small beds or during floods without
additional embankments;
provides coastal fortifications with sufficient water permeability.
|
|
Housing Construction and Maintenance
|
|
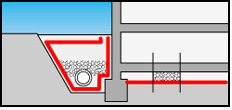
Used as a filtering layer in different drainage
systems
|
prevents flooding of drainage gravel or drainage
pipes by soil particles;
offers high water throughput performance, making the
water to quickly divert to a drainage system;
serves as a separating layer between the soil and
rubble;
prevents mixing of gravel with soil and thus
performs the function of protection, filtering and load balancing;
dredging is now negligible due to small thickness of
the structure;
relieves the load-bearing structures and is easy to install thanks to
its light weight.
|
|
Construction of Railways
|
|
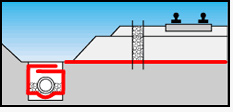
Forms a separating layer between the lower ground
and embankment
|
prevents flooding of the roadbed by fine particles,
thereby the roadbed maintains load balancing and provides load-carrying
capacity;
prevent uneven penetration of subgrade into the
soil, helping to reduce material consumption;
optimizes the seal so that the roadbed does not
penetrate into the soil base;
forms a protective layer that prevents the
penetration of the smallest particles under dynamic loading of the ballast
material;
utilized as a filter between the ground and the
drain filler;
averts flooding of drainage or the drainage pipe by soil
particles;
allows water to pass the drainage system unimpededly;
forms a reinforced layer on soft and non-cohesive
soils;
enhances the stability of the roadbed;
improves the load-bearing capacity.
|
|
Construction of Pipelines for Liquids and Gas transportation
|
|
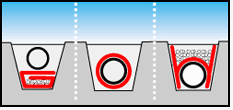
Forms a separating layer between the grounds
|
thanks to the ability to prevent contamination of the ballast
material, its load-distribution capabilities does not change.
|
|
Pools, Ponds, Irrigation Canals,
Rivers
|
|
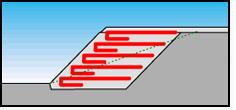
Used for reinforcement of fine-grained soil,
protection of waterproofing materials, inverse filter
|
safeguards waterproofing during installation;
protects waterproofing from uneven ground and diverts
ground water;
prevent water erosion of slopes in case of a drop in
the water level in reservoirs or canals.
prevent the collapse of the slopes;
lowers high pore pressure of the soil.
|
|
Construction of drainages
and sports grounds
|
|
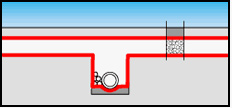
Used as a filter in various drainage systems
|
prevents flooding of drainage aggregate or drainage
pipes by soil particles;
allows water to pass drainage system freely;
serves as separating layer between aggregate and
ground or sports surfaces (grass, sand, etc.);
prevents mixing with soil or aggregate coating and
serves as drainage or load balancing;
dredging is negligible due to small thickness of structure.
|
|
Agriculture
|
|
Widely used in agricultural land
|
protects plants;
mulches;
inhibits weeds growth;
reduces evaporation from soil surface, while
retaining retain moisture;
provides soil with resistance to erosion;
protects crops from birds,
reduces amplitude difference in temperature, reduces
amount of evaporation from soil.
|